Virtual Memory
update 2017-11-15 11:00:15
Memory fragmentation:
只有一部分 heap is “used”。process中每个内存块都需要比实际数据大,没有利用到的内部的空间叫做 "internal fragmentation"。process 之间的在 global memory map 中没利用到的空间叫做 external fragmentation。
Fragmentation 可以由于 fixed page size, buddy system, 和 reclamation(process exit,heap 释放,留下fragment) 造成。我们没有办法 eliminate fragments,因为我们不知道 pointers 在哪里。
造成 Fragmentation 的原因有三点:
- Fixed page size: program的size不是 page size 的整数倍,所以会留下剩余,这是 internal fragmentation;
- Buddy system: 分配的空间是 power of two pages,这是 internal fragmentation;
- Reclaimation: 程序退出会释放内存,在 physical frame 中留下 holes,造成 external fragmentation;
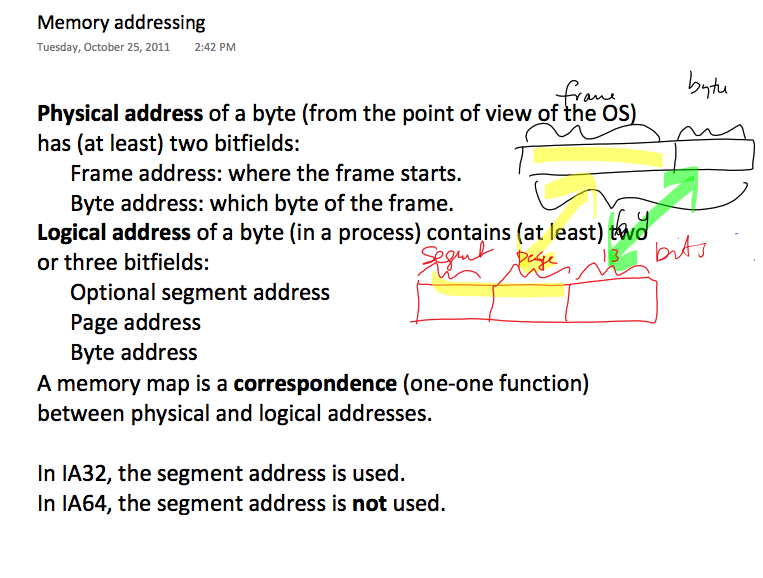
Memory mapping:
- A frame is a unit of memory in the OS;
- A page is a unit of memory in the process;
- Memory mapping associates (os) frames with (process) pages;
- The OS has to maintain data on what gets mapped where;
- What frame goes with what process/page?
Special handling instructions for pages: read-only,shared, private,...



Virtual memory:

- Process run 的时候只有一部分 pages resident;
- 如果一个page is needed and isn't resident:
- block the process
- swap in the required page
- unblock the process after the page is resident(it returns to the run queue)
如果map时,有 unused frame,则将需要的contents从disk中读到这里,然后map到process page。否则,就将一个已经使用的frame unmap,按需要将其存入disk,然后用这个frame存新的。
The dirty bit: 如果memory page 和 disk 中不同,则需要 flush to disk before reuse。 
LRU:
Optimal if memory access is linear, and increasing;
LFU:
Optimal for loops;
题点
Why is it practical to relocate a frame to another physical address?
A frame gets mapped to a page. Its physical address can thus be moved and the logical address stays the same. In fact, this always happens when the page is recovered from disk;
Why is it impractical to relocate a heap page to another address?
因为我们不知道有哪些指针正指向他们。
保持很多休眠processes会不会 slow down the OS?
只有一点慢。因为 process 的 pages 都已经 swapped out,而且 processes 都不在 run queue 中了。内存中只剩下 process page tables,会拖慢一点点。