Dead Lock
update 2017-11-13 11:25:03
Common forms
产生原因
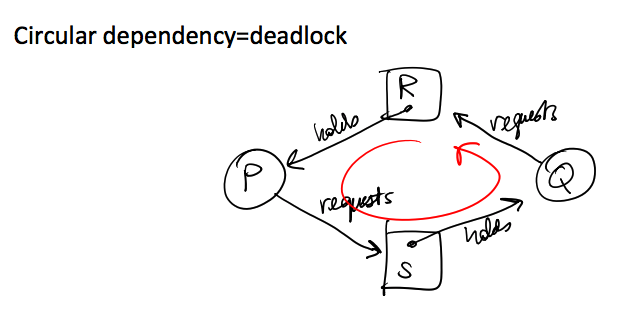
- Circular dependencies: processes waiting for one another;
- Resource saturation/starvation: not enough resource for any one to continue;
两种情形:
- Deadlock of threads in a process;
- Deadlock of processes in an operation system;
Deadlock schedule:
A sequence of events in time that create a deadlock. Deadlock depends upon what happens when, it is often a chance occurrence.
Completion schedule:
A sequence of events in time that demonstrates that a situation is not a deadlock. A situation is not a deadlock if there is any schedule of events under which computation can complete.
基本假设和deadlock
Assumption:
- 进程所申请的资源都是其需要的资源; 2. 当进程获得所有需要的资源后,他一定会完成并且释放资源,没有 outside influences.
Deadlock when:
进程需要资源,而它们在无 outside intervention(ctrl-d) 时不会结束时。
Deadlock 的产生
- Circular dependency: 1. If every process ask for everything it needs all at ones, deadlock cannot occur. 2. 产生deadlock的原因是: processes waits for some resources but already holds others.
另一种是 Resource starvation:
是 circular dependency 的一种特殊情况,对于resource的需求供不应求。多在 incremental allocation 中产生 deadlock。 例如:

Poor understanding of I/O:
Important to remember
When a process awaits resources, it not ready or runnable. 因为它被block,它无法在runtime 纠正自己,所有的纠正 has to come from outside.
Resource allocation graph

Keys to deadlock prevention: Atomicity of allocation
- Request resources all at once;
- Avoid resource allocation races;
- 这就是允许同时做多个semaphore操作的深层原因。
OS deadlock prevention methods
- 提供atomic multi-resource locks (semp);
- 给lock设定优先级,如此避免circular dependency;
- Detect and break deadlock proactively;
Grant lock 和 resource 之前先 analyze;
检测binary lock 的 deadlock
Compute resource allocation graph,如果有环,则有deadlock。在linux中,系统会随机kill一个process来解决。判断是否有环的方法和topological sort类似,可以每次把indegree为0的node去掉,如果最后还剩下node没有去掉,则说明有环。
Next Class
Three approaches to deadlock prevention:
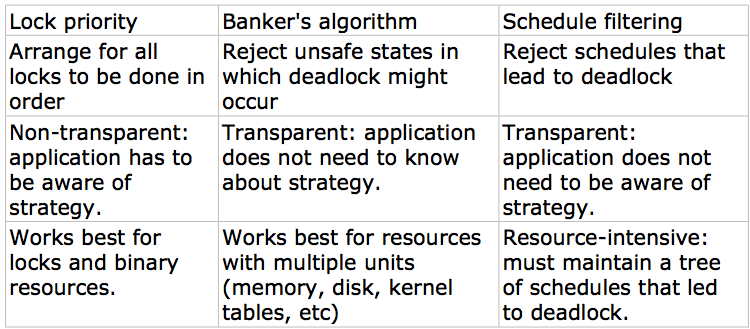
-->Banker's algorithm:

---Attributes of algorithm:
- Paranoid and Pessimistic: assumes the worst about processes;
- Incremental: resource needs not be known about it;
- Can lead to livelock: it leaves processes that were denied resources in a runnable state;
---Basic Idea of the banker's algorithm:
- The operating system is a banker;
- The banker loans resources to processes;
- The processes pay back the loan by returning the resources;
- Banker's goal is to assure that loans are paid back;
- 当client来索要resource的时候,bank需要确认当前剩余resource可以足够current loans to complete;
---Resource matrices:
- Rows: processes;
- Columns: resources
- At row i, column j: demand or supply of resource j by process i;
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Banker%27s_algorithm 上面讲的很不错。
---What is unsafe?
如果存在一种 completion schedule 可以令所有process最终完成,就是safety, 否则就是 unsafe;
---Employing the algorithm:
- 从一定的状态开始,此时有些process running,有些在等resources;
- get a new request, and compute what would happen if we grant it;
- 如果grant之后使系统进入 safe state (即有可能所有processes都完成),则grant;
---Practicality:
- 事实上我们不需要每次查找合适的schedule;
- 当resource request 增加的时候,把它移向尾部;
- 当resource request 减少的时候,把它移向头部;
So we store the schedule and update it as source requirement change (via bubble sort!); (bubble sort 居然有了用武之地)
所以性能上,需要 O(n^2) 时间initialize整个sequence,然后需要 O(n) per change(step)。If requests are small, the time is on average one step。
---题点
为什么banker's algorithm 要考虑 resources are requested, available and not granted 的情况?
因为当一个process结束的时候,它的resource的释放和重新分配需要时间。事实上在实际应用中会遇到很多异步的requests,而 actual granting 会需要比较长的时间,这期间还会有 requests 进入,形成一种 producer-consumer 的关系。
为什么当 malloc 失败(没有内存资源供分配)时返回 0 而不是直接 kill 当前 process?
虽然现在malloc不成功,不代表等一会也不会成功。根据 banker's algorithm 我们假设所有的 resource 最终都会被释放,所以这里的返回值 0 事实上是 indication that the process should wait.
--> Locking in order:
- Number the locks in increasing order;
Lock in that order;
解释
即使两process的起始lock编号不同,也不会出现deadlock;
- 即使有多个processes按照顺序lock,也不会出现deadlock;
--> Atomic allocation:
If N processes request all resources all at once, then there is no deadlock;
--> Lock prioritization
- 为每个 lock 分配一定的 priority;
- 需要按照 priority 顺序 lock;
- If attempt is made out of order, break 低优先级的 lock,按优先级继续;
http://www.cs.tufts.edu/comp/111/notes/Deadlock_prevention.pdf