Memory Addressing
update 2017-11-15 13:22:26
View of memory:
 Process 只能看到 logical pages,而 OS 则使用 physical memory maps; (not finished)
Process 只能看到 logical pages,而 OS 则使用 physical memory maps; (not finished)
Cache
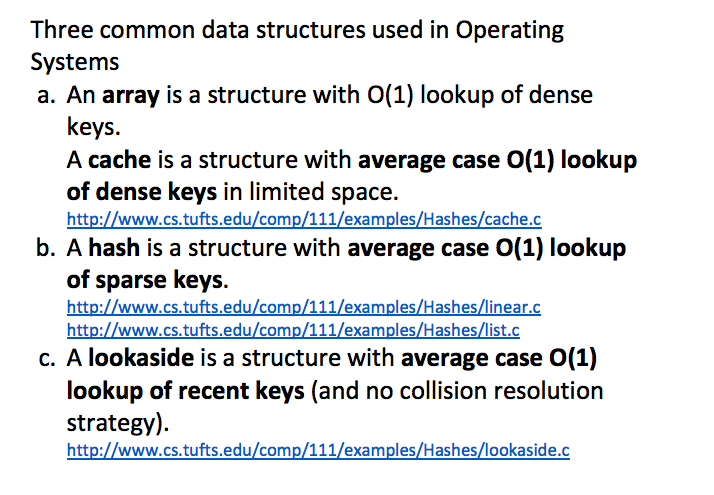
A basic design principle:
- If a correspondence is large and sparse, use a hash.
- If a correspondence is large and dense, use a cache.
- If a correspondence is small, use an array.
Influences upon memory addressing:
- Fragmentation: the fact that allocation patterns create holes in memory space.
- Locality: the fact that most programs access memory with localized patterns of access; the likelihood that apage access will be followed by others is high.
Security: the fact that processes should not be able to
see other processes' space.
Page Tables (IA32)
A page table keeps track of the correspondence between pages and frames. Each logical address is separated into a page number and an offset;
Page table 也有可能不能完全加载,在出现page table cache miss 的时候,会发生如下:
- interrupt the OS
- load a new page table cache entry.
- continue
IA64 不用 page table,而是使用 translation lookaside buffer (TLB)

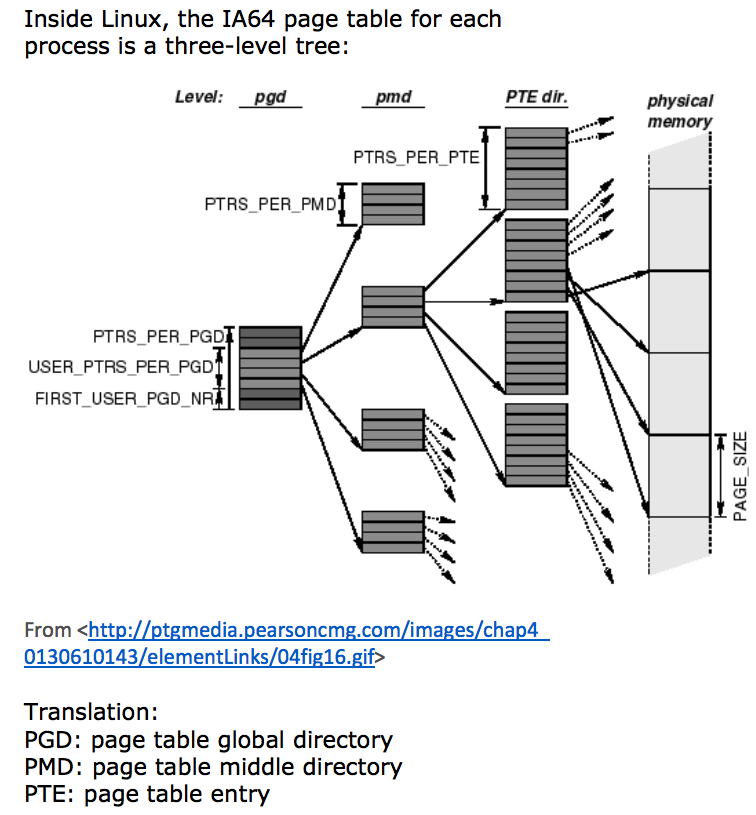
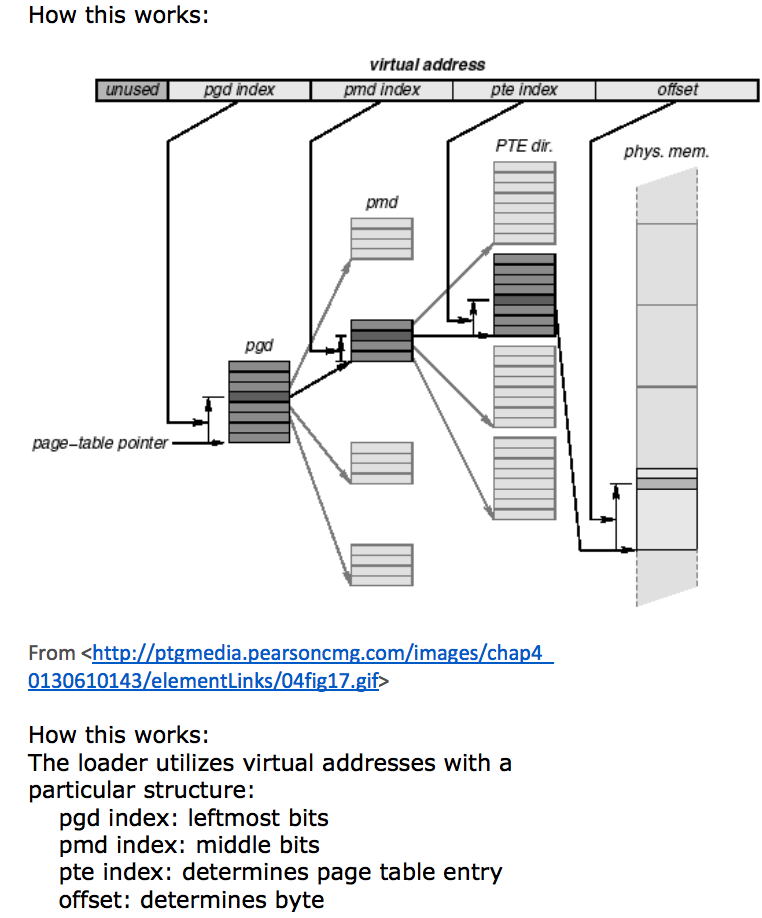
In practice, this is a huge (optimized) array access: table[pgd index][pmd index][pte index] 
Virtual memory

Caches, hashes, and lookasides