How Lock Wait Awake Works
update Jun 14 3:18
Process State
操作系统中的process状态有 created, ready, running, blocked 以及 terminated 几种。

Created
等待 scheduler approve to the “ready” state
Ready( Waiting )
Processes 等待cpu资源,在操作系统中会维持一个"run queue" or "ready queue"。同时需要注意,需要waiting for other resources的process不会被放入"ready queue"
Running
正在执行的process,会在user space和kernel space中进行切换
Blocked
当process在等待资源例如I/O device的时候会被设为blocked state。这种critical sections are protected using a synchronization object such as a semaphore or mutex
Terminated
结束的进程,可能自己结束,也可能被killed。仍然存在于 process table as a zombie process 直到它的parent call wait。如果parent不call wait回收,会持续consume PID,导致resource leak
futex (Fast userspace mutex)
Lock 锁的本质
锁的本质其实是一个公共内存区域中的变量,当一个process或者thread尝试获取一个锁的时候其实是检查这个变量的值并且尝试set它的值。这个 "test and set" 的操作往往可以是由硬件层直接实现的 atomic operation。
wait 的本质
wait的本质其实是将process或者thread的状态设为blocked,直到有某些显式的操作将其唤醒,重新加入 "ready queue",而在这之前,这些blocked process不会消耗CPU资源。
futex 是linux中low level的锁机制实现,它可以在 not contended 的情况下实现 userspace 获取 lock,从而减少切换kernel mode 的频率,提升性能。
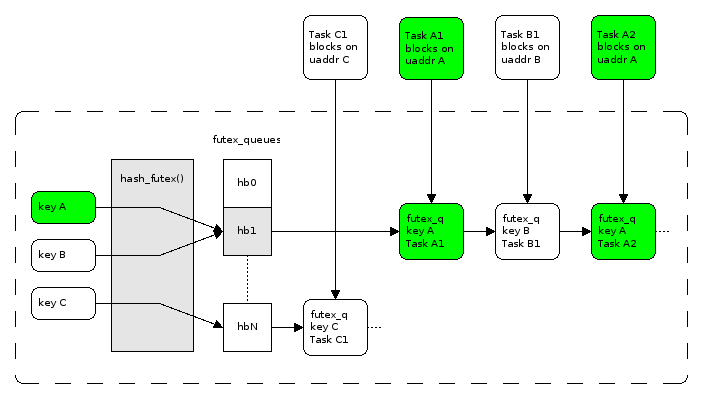
futex的主要操作有 FUTEX_WAIT 和 FUTEX_WAKE。具体的实现方式是: 如果thread或process需要wait for a futex state variable,则需要调用system call进入kernel model。在kernel中会为每个futex variable 维持一个 hash table 中的list,里面存放waiting for this futex value的processes or threads。当有wake操作的时候,进入kernel mode,选择相应当process或者thread将其wake,加入"run queue"。