1192. Critical Connections in a Network
update Oct 31, 2019
There are n servers numbered from 0 to n-1 connected by undirected server-to-server connections forming a network where connections[i] = [a, b] represents a connection between servers a and b. Any server can reach any other server directly or indirectly through the network.
A critical connection is a connection that, if removed, will make some server unable to reach some other server.
Return all critical connections in the network in any order.
Example1:
1 ---- 2
| /
| /
| /
3
|
|
0
Input: n = 4, connections = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,0],[1,3]]
Output: [[1,3]]
Explanation: [[3,1]] is also accepted.
Constraints:
1. 1 <= n <= 10^5
2. n-1 <= connections.length <= 10^5
3. connections[i][0] != connections[i][1]
4. There are no repeated connections.
Basic Idea:
先贴一个youtube链接:Bridge Algorithm
这道题目实际上需要应用一个网络中常用的算法:Bridge Algorithm,用以在一个无向图中寻找所有的critical connection,所谓 critical connection 是指当移除该 edge 的时候会增加图中的联通块数量。
算法的基本思路是对于联通无向图,从任意一点出发做DFS,在DFS的过程中,给每个 visited vertex 依次 label 从小到大的 id 值,并且沿途更新每个 vertex 的 lowLink value。(一个 vertex 的 lowLink value 是指它在DFS中下游遇到节点的最小 label id)。而判断一条边e(u,v)是不是 critical edge,就只要判断 ids[u] < lowLink[v],这样就说明 e(u,v) 是一个 critical edge。
举例说明
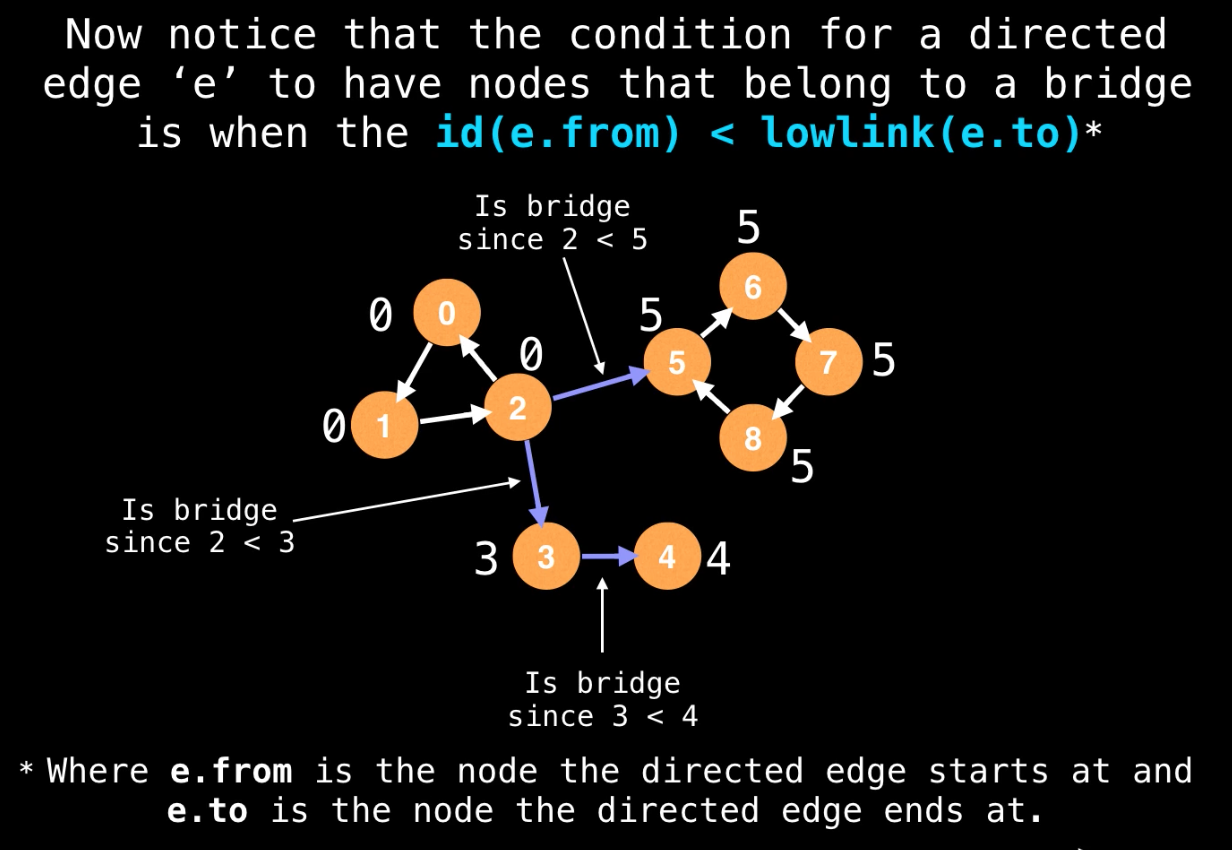
如上图所示,我们从左边的 0 开始 dfs,在到达2时无论是走向0还是走向5或者3,在dfs返回之后,5的lowLink value一定小于 2 的 id,3也一样,还有4. 这样一定能找到三条 critical edges。
Java Code:
class Solution {
private List<List<Integer>> graph;
private List<List<Integer>> res;
private int[] lowLinks;
private boolean[] visited;
private int[] ids;
private int nextId = 0;
private int N;
public List<List<Integer>> criticalConnections(int n, List<List<Integer>> connections) {
res = new ArrayList<>();
N = n;
graph = initGraph(connections);
visited = new boolean[N];
lowLinks = new int[N];
ids = new int[N];
Arrays.fill(lowLinks, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
Arrays.fill(ids, -1);
dfs(0, -1);
return res;
}
private void dfs(int start, int parent) {
visited[start] = true;
ids[start] = nextId++;
lowLinks[start] = ids[start];
for (int neighbor : graph.get(start)) {
if (neighbor == parent) continue; // skip back edge
if (visited[neighbor]) {
lowLinks[start] = Math.min(lowLinks[start], ids[neighbor]);
} else {
dfs(neighbor, start);
lowLinks[start] = Math.min(lowLinks[start], lowLinks[neighbor]);
if (ids[start] < lowLinks[neighbor]) {
res.add(Arrays.asList(start, neighbor));
}
}
}
}
private List<List<Integer>> initGraph(List<List<Integer>> edges) {
List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) ret.add(new ArrayList<>());
for (List<Integer> edge : edges) {
int u = edge.get(0), v = edge.get(1);
ret.get(u).add(v);
ret.get(v).add(u);
}
return ret;
}
}